Healthy recipes and subsidized meal boxes can go a long way in helping child obesity. These are the findings of a study conducted at the University of Gothenburg. The boxes were approved by the families investigated, and as long as the families had access to them, the children’s BMI decreased more than with lifestyle treatment alone.
The aim of the study, published in the European Journal of Pediatrics, was to investigate the effects of a hitherto untested concept in the treatment of childhood obesity: usual lifestyle treatment through counseling combined with healthy recipes and subsidized meal boxes for the whole family.
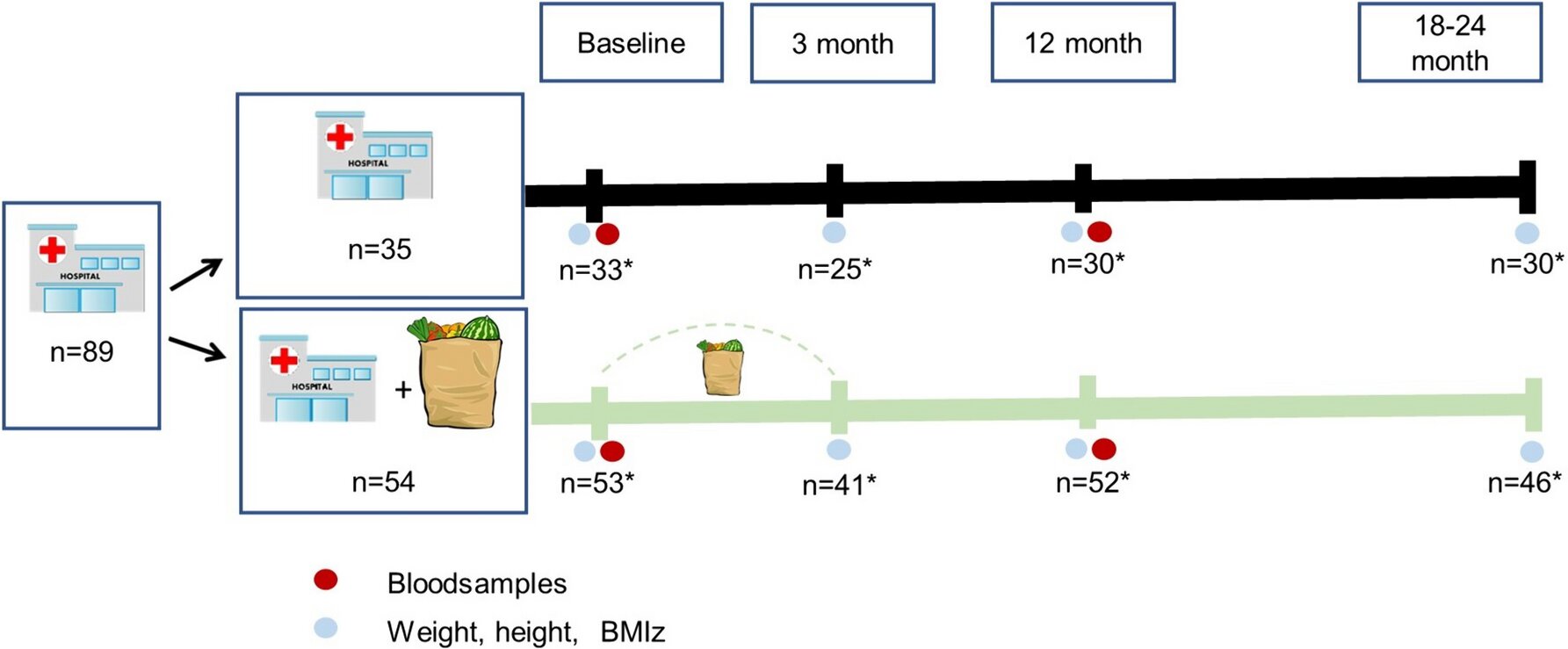
The study included 89 children aged 5 to15 years who were enrolled at one of the child obesity clinics in northern Halland, Sweden. Fifty-four of the children and their families were randomized to receive lifestyle treatment and meal boxes. The remaining 35 children and their families formed the control group and received lifestyle treatment through counseling only.
Every week for three months, the meal box families could pick up recipes and pre-packed boxes with ingredients for five family dinners with the goal of following the Swedish Food Agency’s dietary recommendations. The aim was to involve the whole family and for the dietary treatment to take place at home.
Greater BMI reduction with meal boxes
What was then examined was the children’s BMI at 3, 12 and 18–24 months. A key question was also whether the meal boxes with preselected ingredients would work and be accepted by the families.
One of the main authors in the study is Lovisa Sjögren, a Pediatric Researcher at Sahlgrenska Academy at the University of Gothenburg and a Pediatrician at Halland Hospital Halmstad and Queen Silvia Children’s Hospital in Gothenburg.
“Many people report that it is difficult to cook varied meals from scratch and to have meals together as a family, but this proved to be a tolerable method. The meal box intervention was not perceived as stressful or intrusive, and fights over food shopping and meals were reduced,” she says.
During the meal box period, the first three months, obesity rates decreased more in the meal box families, suggesting that a dietary intervention involving the whole family can be effective. However, at 18–24 months, the greatest BMI reduction was seen in children whose families had only received lifestyle treatment throughout.
Changing diets is difficult and expensive
The meal boxes were heavily discounted with the support of Generation Pep and the ICA Foundation. Local ICA retailers also participated in the packing and delivery of the meal boxes. The researchers believe that the reduced price and tangible support can determine whether a family is able to cope with a dietary change.
“Children are born with a love of movement but some children also have disturbance of their hunger and satiety regulation, and it is important that we also focus on food, not just physical activity. There is a prejudice that all children with a high BMI are sedentary,” says Sjögren.
She believes that Family Meals on Prescription (FMP) with subsidized meal boxes could be established in the same way as Physical Activity on Prescription (PAP) with subsidized exercise activities.
“There is a belief that counseling can change eating habits, but studies show that in practice this is difficult. With this study, we show a workable alternative, although we believe the intervention should be longer.
“There are now new pharmacotherapies to treat obesity during childhood. However before initiating pharmacotherapy we should identify the children for whom a more intensive dietary intervention may be effective,” says Sjögren.
More information:
Terese Torstensson et al, Family meals on prescription as treatment for childhood obesity—a randomized controlled trial, European Journal of Pediatrics (2024). DOI: 10.1007/s00431-024-05744-8
Citation:
Success of meal boxes in treating childhood obesity (2024, September 25)
retrieved 28 September 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-09-success-meal-childhood-obesity.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.