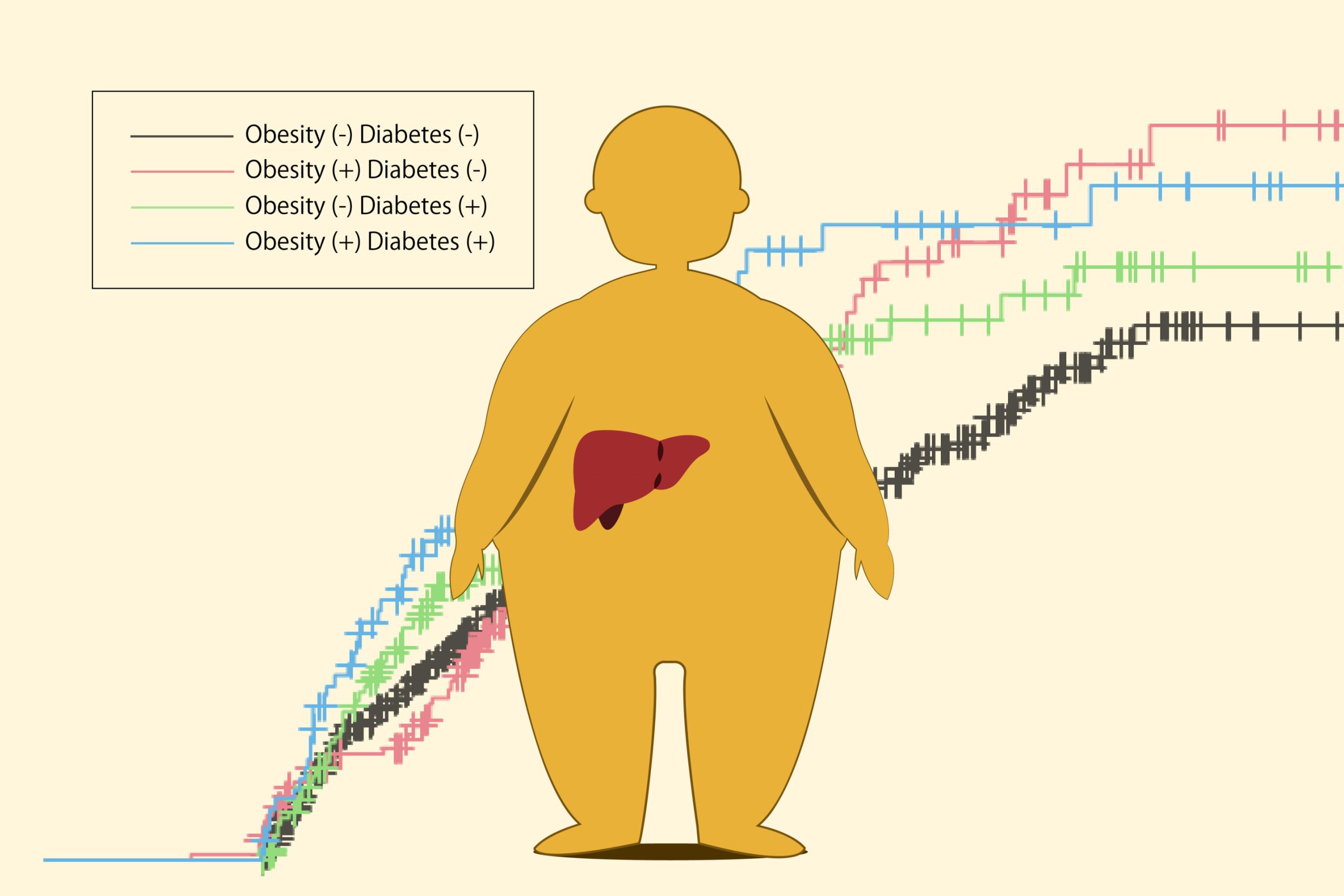
Hepatocellular carcinoma, a type of liver cancer associated with hepatitis infections, is known to have a high recurrence rate after cancer removal. Recent advances in antiviral therapy have reduced the number of patients affected, but obesity and diabetes are factors in hepatocellular carcinoma prevalence. However, these factors’ effects on patient survival and cancer recurrence have been unclear.
To gain insights, Dr. Hiroji Shinkawa’s research team at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine analyzed the relationship between diabetes mellitus, obesity, and postoperative outcomes in 1,644 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who underwent liver resection.
The results, published in Liver Cancer, revealed that the risk of recurrence after two years postoperatively was approximately 1.5 times higher in the case of comorbid obesity and 1.3 times higher in the case of diabetes mellitus.
In addition, the risk of recurrence after five years postoperatively was 3.8 times higher in the case of comorbid obesity and 2.0 times higher in the case of comorbid diabetes alone.
“This study is expected to contribute to the early detection of cancer recurrence and the design of appropriate treatment strategies,” stated Dr. Shinkawa.
“Because the risk of late recurrence is higher in hepatocellular carcinoma with comorbid obesity and diabetes, controlling obesity and diabetes is an important treatment strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma.”
More information:
Hiroji Shinkawa et al, Impact of Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity Comorbidities on Survival Outcomes after Hepatocellular Carcinoma Resection: A Multicenter Retrospective Study, Liver Cancer (2024). DOI: 10.1159/000540858
Citation:
Study ties diabetes and obesity to increased risk of liver cancer relapse (2024, October 3)
retrieved 5 October 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-10-diabetes-obesity-liver-cancer-relapse.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.