Researchers from Niigata University and a University of Pennsylvania team have identified a novel macrolide–DEL-1 axis that helps in bone regeneration and new bone formation. This finding may lead to the development of therapeutic agents to treat bone loss disorders. The study is published in the journal iScience.
Periodontitis is a serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue and destroys the bone that supports teeth. It is usually the result of poor oral hygiene that leads to bacterial infections. Aging may increase susceptibility to periodontitis by altering immune and regenerative functions.
Development endothelial locus-1 (DEL-1), crucial for inflammation resolution and tissue repair, declines with age. The low levels of DEL-1 protein also affect bone regeneration and new bone formation capabilities in the elderly.
In a groundbreaking research endeavor, Research Professor Tomoki Maekawa and a team of researchers from the Center for Advanced Oral Science, Niigata University, Japan, delved into the investigation of age-related periodontitis.
“The motivation behind this study is rooted in the understanding that the prevalence of tooth loss due to periodontal disease and fractures in our super-aging society significantly diminishes the quality of life,” explains Dr. Maekawa.
Their study highlights the ability of erythromycin to stimulate DEL-1 expression, promoting bone regeneration in aging mice. The non-antibiotic derivative EM-523 reproduces these effects. Mechanistically, macrolide treatments enhance bone formation and reduce osteoclasts, suggesting a potential therapeutic avenue for periodontitis-induced bone loss in humans, especially the elderly.
The research team observed a decline in DEL-1 expression with age and found that 12-month-old mice exhibited reduced bone regeneration compared to younger mice. Local microinjections of recombinant DEL-1-Fc in the gingiva of older mice rescued the bone regeneration deficiency.
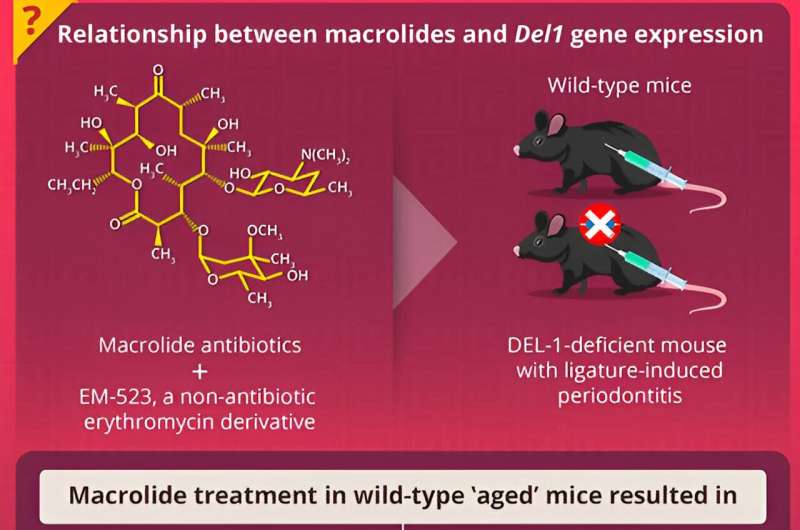
Next, the team administered macrolides antibiotics, particularly erythromycin and its non-antibiotic derivative, EM-523, to 18-month-old “aged” mice and monitored the DEL-1 levels. Interestingly, DEL-1 levels were restored in treated mice and the increased levels of DEL-1 promoted the regeneration of bone that was lost due to naturally occurring age-related periodontitis.
Further in-depth studies demonstrated the promising role of DEL-1, indicating new bone formation in the jaws and related gum tissues through increased alkaline phosphatase activity and osteogenic gene expression. These studies also revealed that macrolides influenced inflammation resolution and reduced osteoclastogenesis in a DEL-1-dependent manner.
Additionally, EM-523 displayed similar effects and enhanced bone mass in femurs. Macrolides promote bone regeneration in aging individuals by modulating the DEL-1 protein, affecting the mesenchymal stromal and stem cell population in the periodontal ligament.
Interestingly, macrolide antibiotics and EM-523 both failed to induce bone regeneration in age-matched DEL-1-deficient mice, confirming that DEL-1 is crucial for the observed bone-regenerating effects of the macrolides.
These findings suggest that targeting DEL-1 expression with macrolides could be a promising approach for promoting bone regeneration in aging individuals. EM-523, with its non-antibiotic properties, emerges as a promising candidate with fewer adverse reactions and the potential to prevent antimicrobial resistance.
The study underscores the significance of understanding the immunomodulatory properties of macrolides for developing safe and effective clinical applications to improve bone regeneration in the elderly population.
“The use of drugs with established safety profiles can lead to the early development of an effective bone regeneration agent. We are hopeful that macrolide-based molecules can be developed further as a treatment option for periodontitis,” concludes Maekawa.
More information:
Kridtapat Sirisereephap et al, A novel macrolide–Del-1 axis to regenerate bone in old age, iScience (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.108798
Citation:
Study finds novel macrolide–DEL-1 axis drives bone regeneration in aging individuals (2024, January 25)
retrieved 28 September 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-01-macrolidedel-axis-bone-regeneration-aging.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.