Currently, kidney transplantation is the most effective treatment to ensure survival and improve the quality of life of patients with end-stage chronic kidney disease, and it is widely practiced in health care systems. However, the monitoring of transplant patients and markers of tolerance to the transplanted organ remain limited.
Available biomarkers are robust but not highly refined, and in most cases, a kidney biopsy is required to make an accurate diagnosis of the organ’s condition and any early signs of rejection. Kidney biopsy is a highly invasive technique and only reveals kidney damage at an already advanced stage.
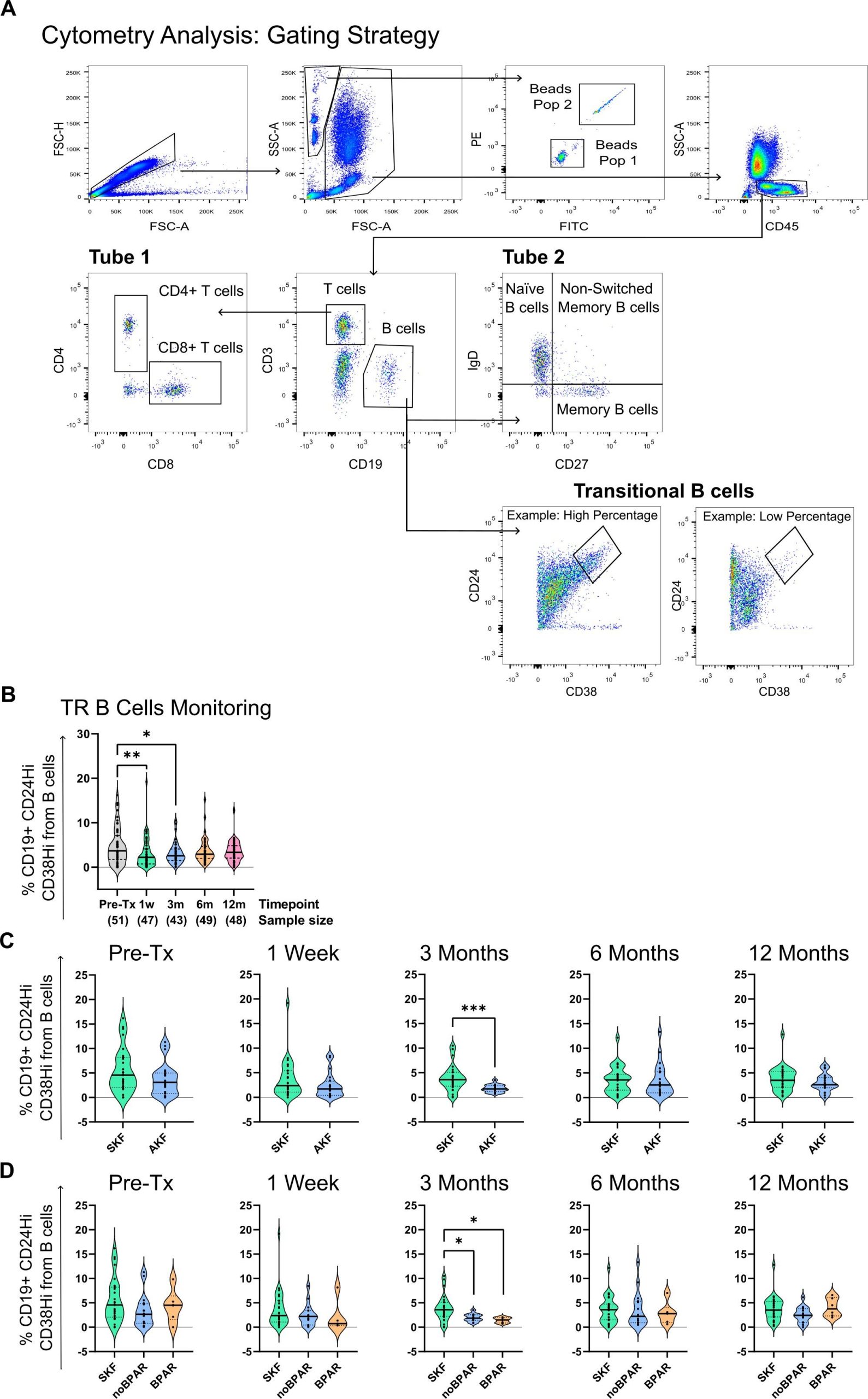
To address these limitations, a study recently published in the journal Frontiers in Immunology explores the use of immune cell analysis, specifically regulatory B cells, to monitor the risk of damage and rejection in kidney transplant patients. The work was carried out by a team of researchers from the Research in Kidney Affecting Diseases Group (REMAR) at IGTP and Germans Trias Hospital, who tracked the progress of around fifty patients over the first year following transplantation.
The longitudinal study allowed them to identify a specific cellular pattern at three months post-transplantation. Patients with higher levels of a specific signature of transitional B cells (associated with regulatory B cells) were found to have a lower risk of future renal dysfunction and rejection, while lower levels indicated a poorer prognosis.
This new signature could allow for more precise tailoring of patient care and treatments. Patients identified as low-risk could benefit from a reduction in immunosuppression regimens, while those at high risk could receive closer monitoring and preventive measures to avoid transplant dysfunction and rejection.
In addition to cellular analysis, the researchers evaluated several genes previously associated by the group with regulatory B cells, which also show a relationship with the functioning of the transplanted kidney and could serve as additional indicators of damage risk.
Sergio Garcia Garcia, a researcher from the REMAR group at IGTP and author of the study, emphasizes the importance of studying the immune system to assess the potential failure of kidney transplants, “Our results are consistent with those observed in previous studies at other centers. It is essential to continue studying B cells and expand the scope to other components of the immune system.”
He adds, “The markers we analyze could have a significant impact on how post-kidney transplant patient monitoring is managed.”
More information:
Inés Perezpayá et al, Molecular screening of transitional B cells as a prognostic marker of improved graft outcome and reduced rejection risk in kidney transplant, Frontiers in Immunology (2024). DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1433832
Provided by
Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute
Citation:
Immune cell analysis helps improve monitoring of rejection risk in kidney transplants (2024, September 27)
retrieved 28 September 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-09-immune-cell-analysis-kidney-transplants.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.