Researchers have for the first time created an integrated single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) atlas of the human periodontium, the specialized tissues in the mouth that connect teeth to the underlying bone. This atlas will help identify the unique environments that impact on the development of gum disease (periodontitis), leading to better and more precise treatments.
Millions of people worldwide experience gum disease (periodontitis). Aside from pain and tooth loss, this disease is also associated with more than 60 systemic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, and inflammatory bowel diseases.
To date, little has been known about the exact combinations of micro-organisms and cell types in the human mouth that affect the body’s immune response, and which contribute to the development of periodontitis.
An international research team, led by Dr. Kevin Byrd at the American Dental Association and including Inês Sequeira from the Institute of Dentistry at Queen Mary University of London, has analyzed samples taken from previously published single-cell RNA sequencing projects to create an integrated periodontitis atlas of human tissues.
This work, published in Nature Communications, builds on the efforts of Dr. Sequeira and Dr. Byrd in creating a comprehensive atlas of the mouth cells, as leader and co-founders of the Oral and Craniofacial Bionetwork of the Human Cell Atlas.
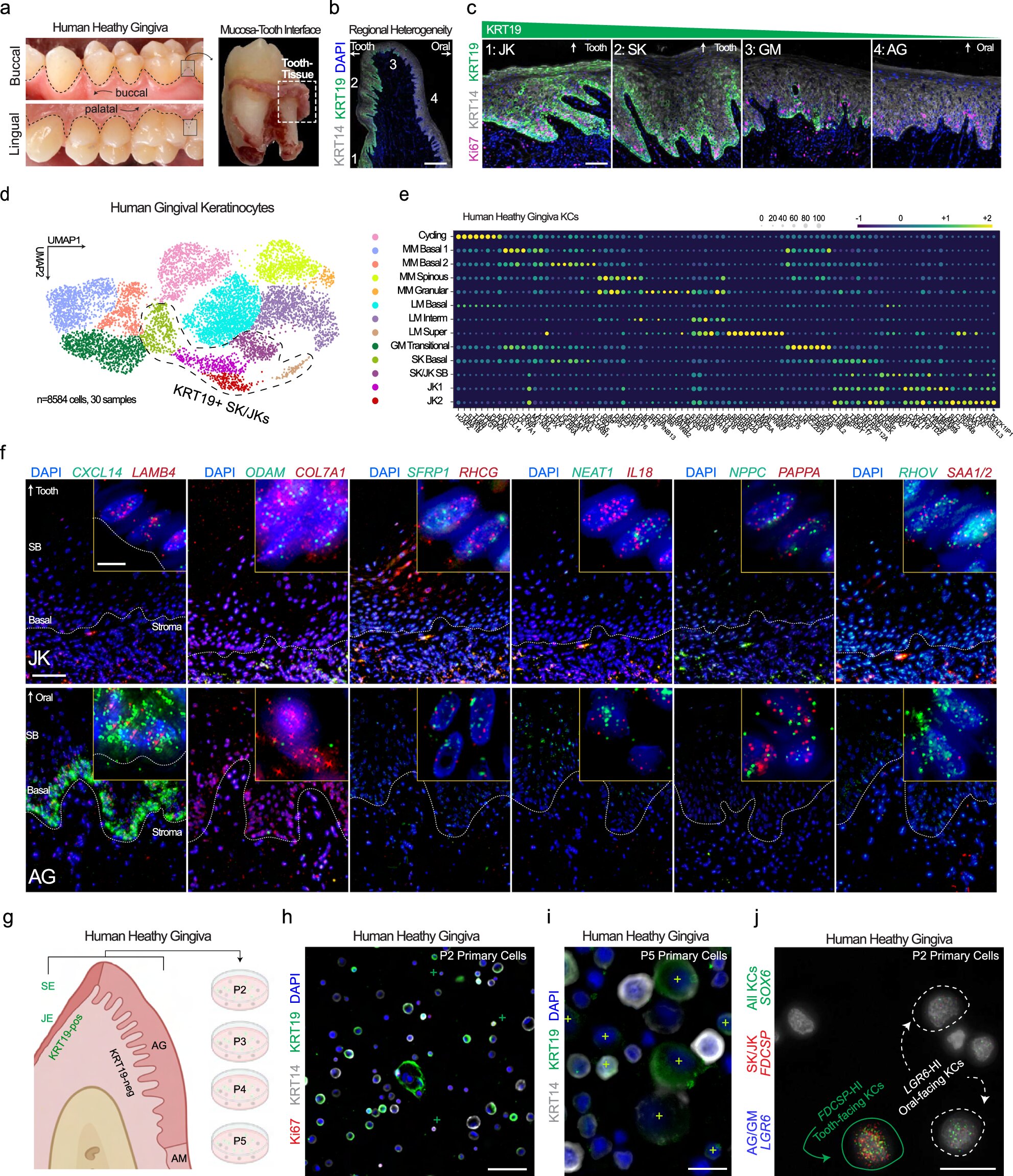
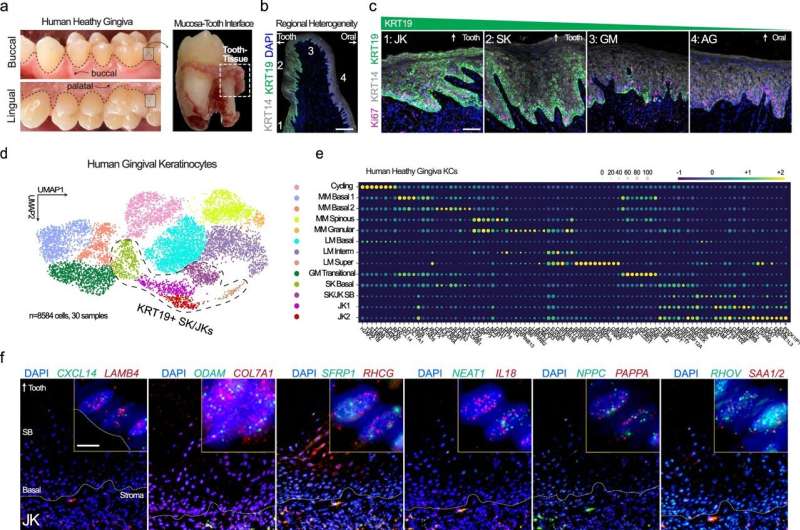
The study describes 17 total and functionally annotating five new gingival keratinocyte subpopulations within the human gingival epithelium at a single-cell level. Furthermore, cross-species analysis also supports the heterogeneity of murine gingival keratinocytes. The heterogeneity of these keratinocytes subpopulations was mapped into spatial context using state-of-the-art multiplex imaging.
Researchers found that tooth-facing sulcular keratinocytes (SKs) and tooth-interfacing junctional keratinocytes (JKs) displayed altered differentiation states and showed greater activation of the proteins necessary for an immune response (cytokines) in periodontitis.
The research identified that the way that these cells maintain the barrier between the microbe-rich environment inside the mouth and the surface of the teeth has a profound impact on the way the body reacts to microbial attack. Further research is needed to support precision periodontal interventions in states of chronic periodontal inflammation.
Dr. Sequeira said, “This research highlights the intricate cell-microbe interactions and immune responses within the periodontal niche, paving the way for precision periodontal interventions to combat chronic inflammation. “
More information:
Quinn T. Easter et al, Single-cell and spatially resolved interactomics of tooth-associated keratinocytes in periodontitis, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49037-y
Citation:
Genetic atlas shows gum disease may be caused by immunosuppression of skin cells in the mouth (2024, June 14)
retrieved 13 September 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-06-genetic-atlas-gum-disease-immunosuppression.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.