A new study in the Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology estimates the incidence of neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS), a potentially fatal adverse effect of antipsychotic treatment, among individuals aged 5–24 years.
Wayne Ray, Ph.D., from the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, and co-authors, used national Medicaid data from 2004–2013 to identify patients beginning antipsychotic treatment and calculated the incidence of NMS during antipsychotic use.
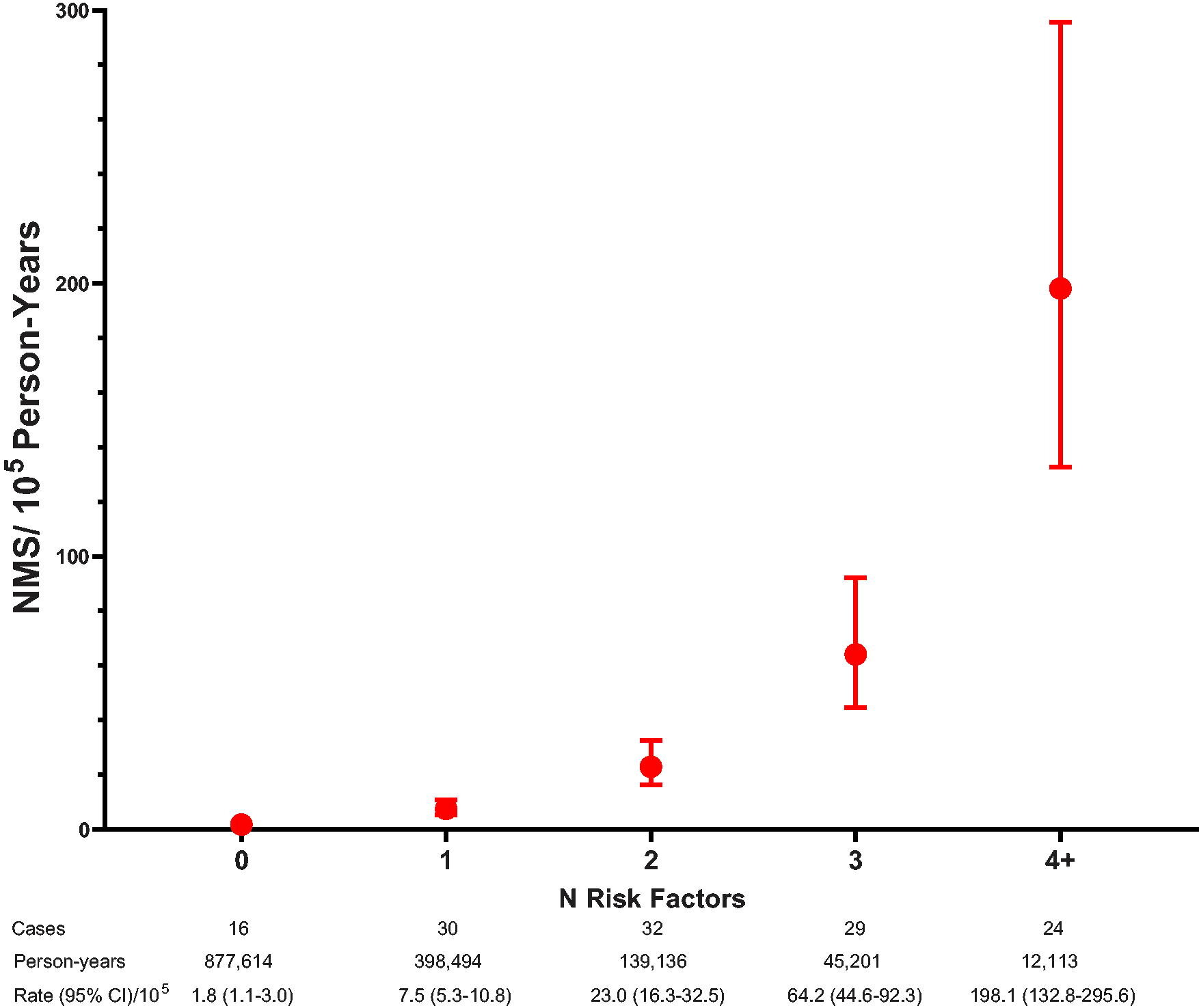
The investigators identified five factors that independently predicted increased NMS incidence: age 18–24 years; schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders; neurodevelopmental disorders; antipsychotic dose >200 mg chlorpromazine-equivalents; and first-generation antipsychotics.
“Patients with four or five of these factors had more than 100 times the incidence of those with none,” reported the investigators.
“These data provide a basis for early identification of children and youth at elevated risk for NMS for whom monitoring for signs of this life-threatening syndrome could be increased, potentially leading to earlier detection and improved outcomes.”
Paul E. Croarkin, DO, MS, editor-in-chief of the Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, says, “Neuroleptic malignant syndrome is rare, serious, and previously understudied in children and adolescents. This important paper by Dr. Ray and colleagues has illuminated risk factors with immediate utility for clinical practice and provided a foundation for future research.”
More information:
Wayne A. Ray et al, Incidence of Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome During Antipsychotic Treatment in Children and Youth: A National Cohort Study, Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology (2024). DOI: 10.1089/cap.2024.0047
Citation:
Estimating incidence of neuroleptic malignant syndrome in youth on antipsychotics (2024, September 19)
retrieved 21 September 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-09-incidence-neuroleptic-malignant-syndrome-youth.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.