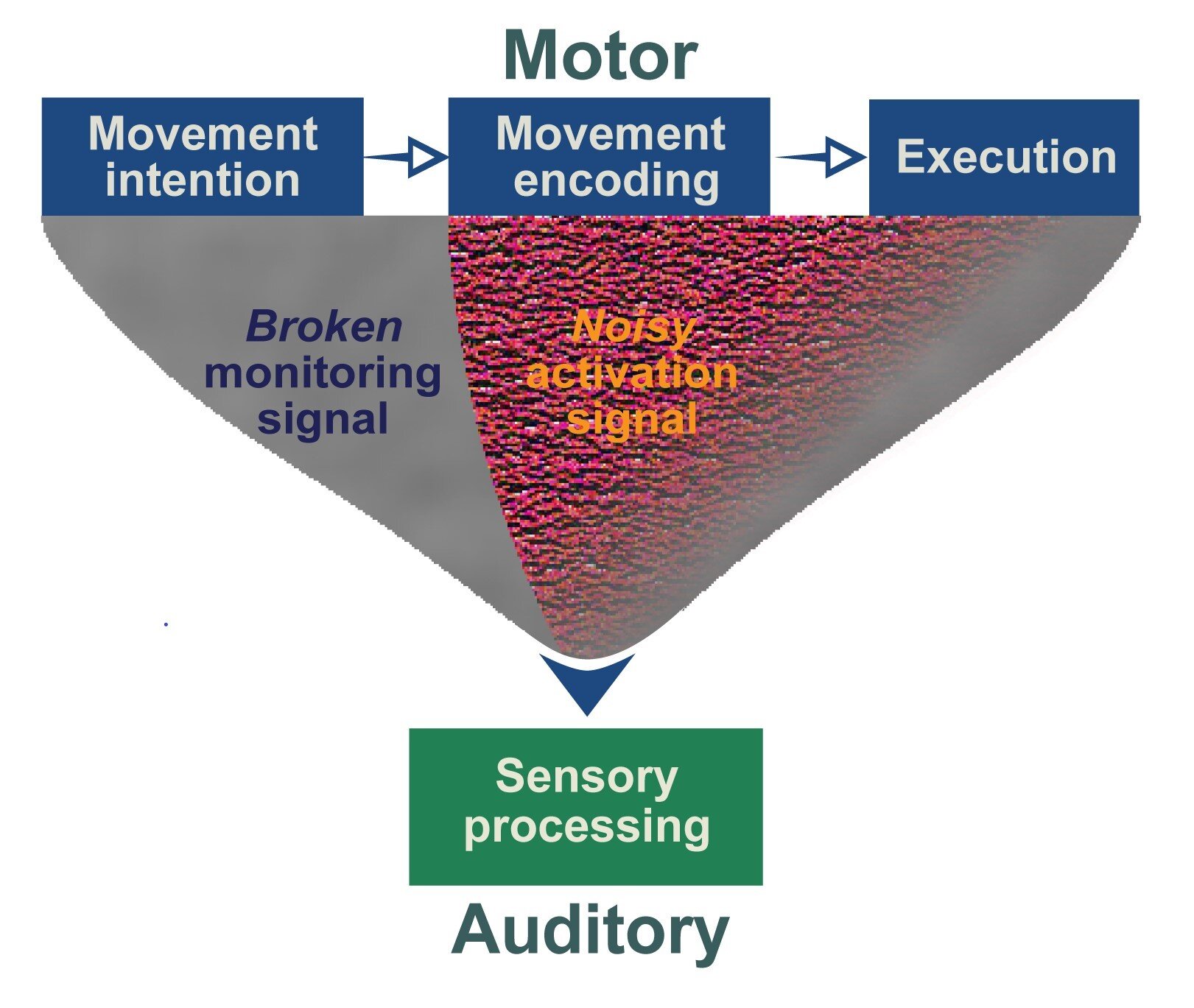
Auditory hallucinations are likely the result of abnormalities in two brain processes: a “broken” corollary discharge that fails to suppress self-generated sounds, and a “noisy” efference copy that makes the brain hear these sounds more intensely than it should. That is the conclusion of a study published October 3 in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Xing Tian, of New York University Shanghai, China, and colleagues.
Patients with certain mental disorders, including schizophrenia, often hear voices in the absence of sound. Patients may fail to distinguish between their own thoughts and external voices, resulting in a reduced ability to recognize thoughts as self-generated.
In the new study, researchers carried out electroencephalogram (EEG) experiments measuring the brain waves of 20 patients diagnosed with schizophrenia with auditory hallucinations and 20 patients diagnosed with schizophrenia who had never experienced such hallucinations.
In general, when people are preparing to speak, their brains send a signal known as “corollary discharge” that suppresses the sound of their own voice. However, the new study showed that when patients with auditory hallucinations were preparing to speak a syllable, their brains not only failed to suppress these internal sounds, but had an enhanced “efference copy” response to internal sounds other than the planned syllable.
The authors conclude that impairments in these two processes likely contribute to auditory hallucinations and that targeting them in the future could lead to new treatments for such hallucinations.
The authors add, “People who suffer from auditory hallucinations can ‘hear’ sounds without external stimuli. A new study suggests that impaired functional connections between motor and auditory systems in the brain mediate the loss of ability to distinguish fancy from reality.”
More information:
Yang F, Zhu H, Cao X, Li H, Fang X, Yu L, et al. Impaired motor-to-sensory transformation mediates auditory hallucinations, PLoS Biology (2024). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002836
Citation:
Brain scan study shows what happens in the brain when a person with schizophrenia hears voices (2024, October 3)
retrieved 6 October 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-10-brain-scan-person-schizophrenia-voices.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.