Worldwide, at least 50 million people are believed to be living with a form of dementia. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia. It is a progressive and irreversible neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects memory and cognitive functions. Symptoms include memory loss that disrupts daily life, poor judgment and taking longer to complete normal daily tasks. There is currently no cure.
The most common form of Alzheimer’s disease is called sporadic Alzheimer’s disease, which occurs due to a complex combination of genes, environment and lifestyle. It has no specific family link.
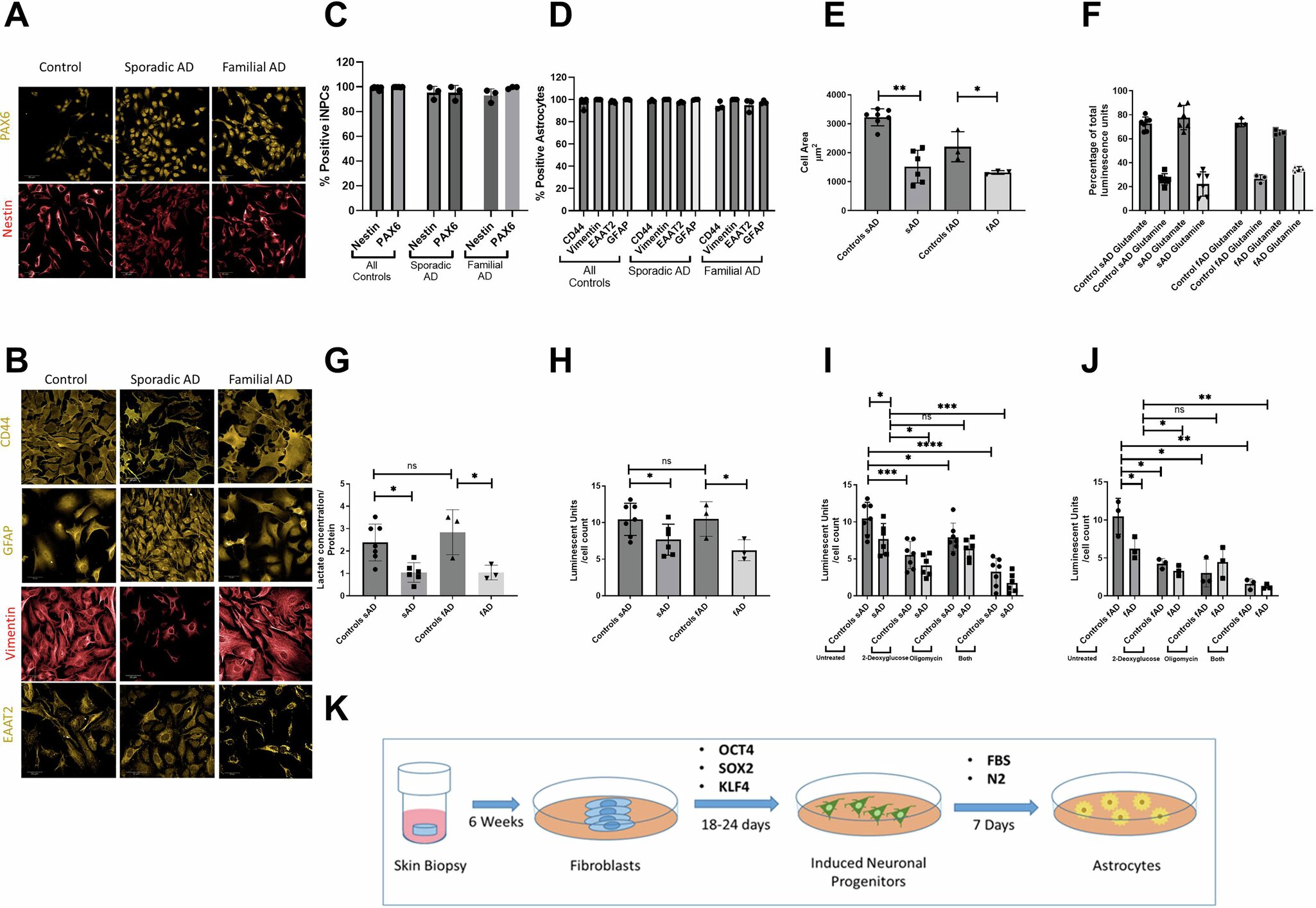
Astrocytes are a subtype of important cells that make up the majority of cells in the nervous system. They perform many functions including providing nutrients, support, and insulation for neurons. Early in Alzheimer’s disease, it has been shown that astrocytes have problems with their metabolism and aren’t able to process information properly, impacting the energy used to help neurons function effectively.
“Most people focus on neurons, but there are actually more astrocytes in the brain than neurons. Once the metabolism of astrocytes becomes perturbed, then the astrocyte definitely will not be able to provide as much support to neurons,” explains Professor Heather Mortiboys from the Neuroscience Institute.
A study undertaken by Dr. Simon Bell from the Neuroscience Institute at the University of Sheffield was the first to identify the impact of damaged astrocytes in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease on cellular power plants known as the mitochondria. The study found that damaged astrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease have less energy production and generate more stress on the mitochondria.
The work is published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry.
Crucially, the study discovered that a key enzyme called hexokinase 1 (HK1) was lower in astrocytes from people with sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. The study revealed that by boosting this enzyme, it was possible to improve the energy of astrocytes in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease and reduce the negative impact of abnormal astrocytes.
The study was undertaken by Dr. Simon Bell and led by Professor Mortiboys. The study involved many researchers, including Hollie Wareing, Francesco Capriglia, Rachel Hughes, Katy Barnes, Alexander Hamshaw, Dr. Liam Adair, Allan Shaw, Alicja Olejnik, Suman De, Elizabeth New, Professor Dame Pamela J. Shaw, Dr. Matteo De Marco, Professor Annalena Venneri, Dr. Daniel J. Blackburn, and Laura Ferraiuolo.
“For this study, we took samples from patients with sporadic Alzheimer’s disease via a skin biopsy and grew skin cells, or fibroblasts, in the lab. We then used reprogramming techniques to turn them into stem cells and differentiate them into astrocytes,” explains Professor Mortiboys.
“When comparing the astrocytes between sporadic Alzheimer’s and familial Alzheimer’s, we found key changes in the mitochondria. As well as being a different shape and size, there are also changes in the glycolytic pathways which means the astrocytes have an overall energy deficit. The study highlights the different mechanisms at play between sporadic and familial Alzheimer’s and how boosting HK1 could improve cell metabolism in early Alzheimer’s,” she adds.
The research suggests that problems in astrocyte metabolism may occur early in Alzheimer’s disease and highlights the potential role of HK1 in these processes.
More information:
Simon M. Bell et al, Increasing hexokinase 1 expression improves mitochondrial and glycolytic functional deficits seen in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease astrocytes, Molecular Psychiatry (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41380-024-02746-8
Citation:
Astrocytes study identifies a new therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease (2024, September 23)
retrieved 7 October 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-09-astrocytes-therapeutic-alzheimer-disease.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.