Uncommon Courses is an occasional series from The Conversation U.S. highlighting unconventional approaches to teaching.
Title of course:
“Intoxication Nation: Alcohol in American History”
What prompted the idea for the course?
I wanted to get students excited about studying the past by learning about something that is very much a part of their own lives.
Alcohol – somewhat surprisingly to me at first – featured prominently in my own research on minority rights and U.S. democracy in the mid-19th century. As a result, I knew quite a bit about the temperance movement and conflicts over prohibition during that period. Designing this course allowed me to broaden my expertise.
What does the course explore?
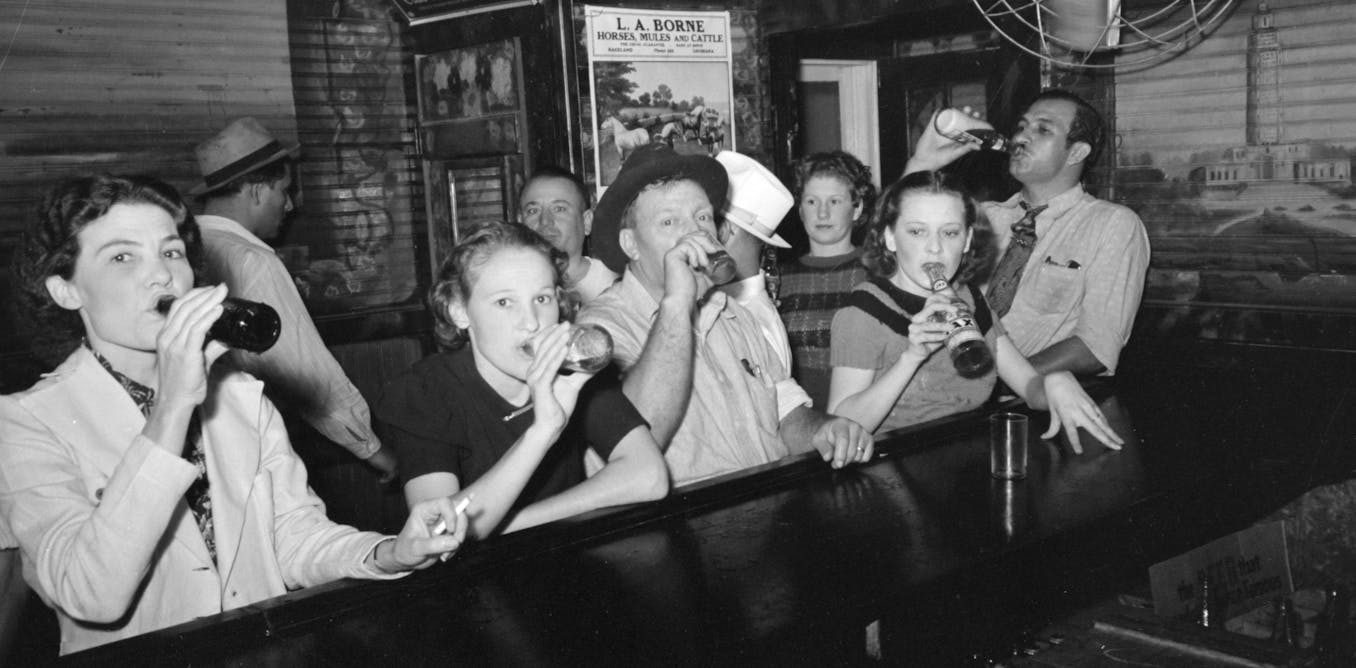
Prohibition is a must-do subject. Students expect it. But I cover several hundred years of history: from the 17th-century invention of rum – as a byproduct of sugar produced by enslaved people – to the rise of craft beer and craft spirits in the 21st century.

Office of Naval Records and Library via National Archives Catalog
Along the way, I’m thrilled when students get excited about details that allow them to taste a more complicated historical cocktail. For example, they learn why white women’s production of hard cider was crucial to the survival of colonial Virginia. The short answer: Potable water was in short supply, alcoholic drinks were far healthier, and white men – and their indentured and enslaved workforce – were busy raising tobacco. It fell to women to turn fruit into salvation.
Why is this course relevant now?
Alcohol remains a big and almost inescapable part of American society. But of late, Americans have been drinking differently – and thinking about drinking differently.
Examples abound. Alcohol producers, we learn, now face competition from legalized weed. Drinking levels rose during the COVID-19 pandemic, yet interest is declining among Gen Zers. The “wine mom” culture that brought some mothers together now faces mounting criticism.
And, of course, there’s the never-ending debate about the health benefits and risks of alcohol. Of late, the risks seem to be dominating headlines.
What’s a critical lesson from the course?
Alcohol has been a highly controversial, central aspect of the American experience, shaping virtually all sectors of our society – political and constitutional, business and economic, social and cultural.
What materials does the course feature?
What will the course prepare students to do?
Like any history course, this one aims to develop student’s analytical, written, research and verbal skills. In lots of ways, the topic is just a tool to get students to grow their brains. But I also seek to grow students’ critical awareness of the place of alcohol in their own lives. The course has also informed students’ paths after graduation – including some who wound up working in the alcohol industry or recovery organizations.