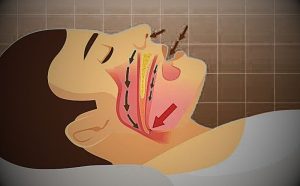
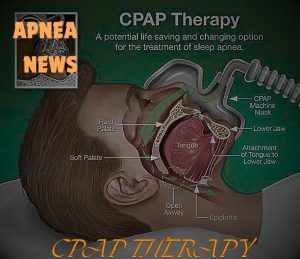
Treatments and Therapies
Some medical treatments that may help include:
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP):A CPAP machine continuously blows air into the throat via a mask worn over the nose (or the nose and mouth), keeping the airway open. It helps a person breathe during sleep by “stenting” the upper airway open with pressurized air.
Surgery:Surgery can address structural issues in the mouth and upper airway by removing excess tissue or reshaping the airway.
Oral appliances:Certain appliances can help keep the airway open by preventing the tongue from falling back against the soft palate.
Medications:Some medications can help with daytime sleepiness if it persists after adequate treatment, but they do not address the underlying sleep apnea.
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy is a common treatment for obstructive sleep apnea.
What is CPAP
CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) is a machine that uses mild air pressure to keep breathing airways open while you sleep.
Your healthcare provider may prescribe CPAP to treat sleep-related breathing disorders including sleep apnea. CPAP also may treat preterm infants who have underdeveloped lungs.
What does a CPAP machine include?
A CPAP machine includes:
A mask or other device that fits over your nose or your nose and mouth
Straps to position the mask
A tube that connects the mask to the machine’s motor
A motor that blows air into the tube
How does CPAP work?
You should use your CPAP machine every time you sleep at home, while traveling, and during naps.
Getting used to using your CPAP machine can take time and requires patience. Your healthcare provider will work with you to find the most comfortable mask that works best for you.
You may also need help from your healthcare provider to use the humidifier chamber in your machine or to adjust your pressure settings. You may also need to try a different machine that has multiple or auto-adjusting pressure settings.
For the treatment to continue to work, it is important that you clean your mask and tube every day and refill your medical device prescription at the right time to replace the mask and tube.
What are the benefits of CPAP?
You may notice immediate improvements after starting CPAP treatment, such as better sleep quality, reduction or elimination of snoring, and less daytime sleepiness.
Equally important are the long-term benefits of CPAP, which include:
Helping to prevent or control high blood pressure
Lowering your risk for stroke
Improving memory and other cognitive function
What are the possible side effects of CPAP?
Side effects of CPAP treatment may include congestion, runny nose, dry mouth, or nosebleeds.
Some masks can cause irritation. Your healthcare provider can help you find ways to relieve these symptoms and adjust to using your CPAP machine.
If you experience stomach discomfort or bloating, you should stop using your CPAP machine and call your healthcare provider right away.
Is CPAP covered by insurance?
If your healthcare provider prescribes CPAP for sleep apnea, your insurance will work with a medical device company to provide you with a CPAP machine and the mask and tube.
Your provider will set up your machine with certain pressure settings. After using your machine for a while, your provider and possibly your insurance company will want to check the data card from your machine to confirm that you are using your CPAP device and to see if the machine and its pressure settings are working to reduce or eliminate apnea events while you sleep.
CPAP machines: Tips for avoiding 10 common problems
CPAP is an important treatment for obstructive sleep apnea, but it may be frustrating at first. Learn how to avoid uncomfortable masks and other common CPAP problems.
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy is a common treatment for obstructive sleep apnea. A CPAP machine uses a hose connected to a mask or nosepiece to deliver constant and steady air pressure to help you breathe while you sleep.
Common problems with CPAP include a leaky mask, trouble falling asleep, a stuffy nose and a dry mouth.
But if a CPAP mask or machine doesn’t work for you, you have other options. And most CPAP masks can be adjusted to help make them more comfortable.
Here are 10 common CPAP problems and what you can do about them:
Work closely with your healthcare professional and the CPAP supplier to make sure you have a CPAP mask that fits properly. People have different face shapes, so the right mask style and size for someone else may not work for you.
Try a different mask. A range of CPAP masks is available. For example, a full face mask covers the mouth and nose, with straps that stretch across the forehead and cheeks. These may make some people feel claustrophobic, but they work well for those who prefer to breathe through their mouths during sleep. They also provide a stable fit for people who move around a lot during sleep.
Other masks feature nasal pillows that fit under your nose and straps that cover less of your face. These can feel less cumbersome.
Nasal pillows may work well if you wear glasses or read with the mask on because some don’t block the eyes as much as full face masks do. However, this mask style may not be an option if you move around a lot during sleep or have difficulty breathing through your nose, such as due to congestion.
Pay attention to size. Most masks come in different sizes. Just because you’re a certain size in one mask doesn’t mean you’ll be the same size in another. CPAP masks are usually adjustable.
Ask your healthcare professional or CPAP supplier to show you how to adjust your mask to get the best fit. Manufacturer product instructions also can help show you how to do this. A properly fitting mask shouldn’t be uncomfortable or cause pain.
First, try wearing just the CPAP mask for short periods of time while you’re awake — for example, while watching TV. Then try wearing the mask and hose with the machine turned on during the day while you’re awake.
Once you get used to how that feels, start using the CPAP machine every time you sleep — including during naps. Only using the CPAP machine every now and then may delay getting used to it. Stick with it for several weeks or more to see if your mask and pressure are right for you.
You may be able to overcome this by using a machine with a “ramp” feature. This setting allows you to start with low air pressure. The machine then automatically and slowly increases the air pressure to your prescribed setting as you fall asleep. Your healthcare professional can adjust its rate.
If this feature doesn’t help, talk with your healthcare team about changing to a machine that automatically and constantly adjusts the pressure while you’re sleeping. An example is a bi-level positive airway pressure (BPAP) machine that delivers more pressure when you breathe in, called inhale, and less when you breathe out, called exhale.
Check to make sure your mask fits well. A leaky mask can dry out your nose. If you have to tighten the straps often to prevent air leakage, the mask does not fit properly.
A CPAP machine that features a heated humidifier, which attaches to the air pressure machine, can help. You can adjust the level of humidification. Using a nasal saline spray at bedtime also can help ease a dry, stuffy nose.
Practice using your mask while you’re awake. First, just hold it up to your face without any of the other parts. Once you’re comfortable with that, try wearing the mask with the straps.
Next, try holding the mask with the attached hose on your face, without using the straps. Turn on the CPAP machine, perhaps with the ramp feature turned on. Next, do this using the straps too. Finally, try sleeping with the mask and machine on.
Relaxation exercises, such as progressive muscle relaxation, may help reduce anxiety related to CPAP use.
If you’re still feeling claustrophobic, talk with your healthcare professional or CPAP supplier. It may help to get a different size mask or try a different style, such as one that uses nasal pillows.
A leaky or an ill-fitting mask means you’re not getting the full air pressure you need, and it may be irritating your skin. The mask also can direct air into your eyes, causing them to become dry or teary.
Try adjusting pads and straps to get a better fit. If the mask fits over your nose, make sure it doesn’t sit too high on the bridge of your nose, which can direct air into your eyes.
You may need to ask your CPAP supplier to help you find a different size mask, particularly if your weight has changed a lot. Or try a different style mask such as one that uses nasal pillows. If you develop skin deterioration or sores, such as on your nose, tell your care team promptly.
Wearing the mask alone for some time during the day may help you get used to how it feels and make it easier to fall asleep at night.
Machines with the ramp feature that slowly and gradually increase the air pressure to your prescribed pressure setting as you fall asleep may make you more comfortable at bedtime.
Following good general sleep habits also is helpful. Exercise regularly and avoid caffeine and alcohol before bedtime. Try to relax. For example, take a warm bath before you go to bed. A white noise machine may help.
If you breathe through your mouth at night or sleep with your mouth open, some CPAP machines may worsen dry mouth. A chin strap may help keep your mouth closed and reduce the air leak if you wear a nasal mask.
A machine with a full face mask that covers your mouth and nose also may work well for you. A CPAP-heated humidifier that attaches to the air pressure machine also may help.
It’s not unusual to sometimes wake up to find that you’ve removed the mask in your sleep. If you move a lot in your sleep, you may find that a full face mask will stay on your face better. You may have removed your mask while sleeping because you were uncomfortable. Consider trying a different type of mask that may fit you better.
You may be pulling off the mask because your nose is congested. If so, ensuring a good mask fit and adding a CPAP-heated humidifier may help. A chin strap may help keep the mask on your face.
If removing the mask is a consistent problem, consider setting an alarm for a time during the night so you can check whether the mask is still on. You could progressively set the alarm for later in the night if you find that you’re keeping the mask on longer.
Most new models of CPAP machines are almost silent. But if you find that your machine’s noise is bothersome, first check to make sure the machine’s air filter is clean and unblocked. Something in its way may worsen noise. Ask your healthcare provider or CPAP supplier how to properly clean your mask and hose.
If cleaning doesn’t help, have your care team or CPAP supplier check the machine to ensure it’s working properly. If the machine is working correctly and the noise still bothers you, try wearing earplugs or using a white noise machine to mask the noise. Placing the CPAP machine as far away from the bed as possible also may help make any machine noise less noticeable. Ask your healthcare professional or CPAP supplier if extra tubing is available and right for your machine.
Using a CPAP machine can be frustrating as you try to get used to it, but it’s important that you stick with it. The treatment is essential to avoiding complications of obstructive sleep apnea, such as heart problems and excessive daytime sleepiness.
Work with your care team and CPAP supplier to ensure the best mask fit and device for you. Regular visits to your healthcare professional are important and can help troubleshoot any problems and adjust settings, if needed. It can take a while to find the correct settings and get used to the mask.
With time and patience, CPAP can positively affect your quality of life and health.